Most often, inflammation of the prostate gland is caused by various infections that fall into it from the bladder, urethra or rectum.Prostatitis can also be a complication of tonsillitis, influenza, tuberculosis.
Treatment of prostatitis requires an integrated approach to get rid of the symptoms of this disease and avoid complications, you must consult a doctor, and not self -medicate.
What is it?
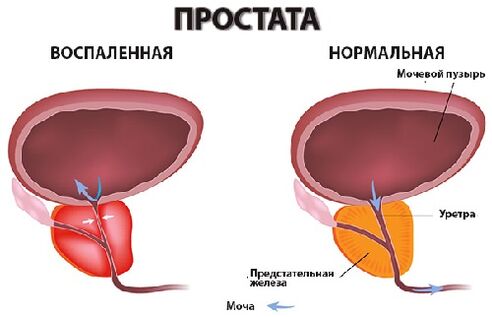
Prostatitis - inflammation of the seed (prostate) gland - prostate.It is manifested by frequent urination with an admixture of blood, pus in the urine, pain in the area of the penis, scrotum, rectum, sexual disorders (violation of erection, early ejaculation, etc.), sometimes delayed urine.Perhaps abscessing the prostate gland, inflammation of the testicles and appendages, which threatens infertility.The ascent of the infection leads to inflammation of the upper parts of the genitourinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis).
Treatment of prostatitis varies depending on what form of the disease occurs in a man.So, bacterial prostatitis can occur both in acute form and as a chronic disease.Quite often, non -bacterial prostatitis is also diagnosed as a chronic ailment.Such a variety of prostatitis is also called a syndrome of chronic pelvic pain.In such patients, all symptoms characteristic of prostatitis are observed, but there are no bacteria in the secret of the prostate.
Prostatitis develops with the penetration of an infectious agent, which enters the prostate tissue from the organs of the genitourinary system (urethra, bladder) or from the remote inflammatory focus (with pneumonia, influenza, tonsillitis, furunculosis).
There are a number of risk factors that increase the likelihood of prostatitis.

Why does prostatitis develop?
Currently, the reasons for the development of prostatitis are divided into two large groups:
- Infectious(infections transmitted sexually (penetration into the tissue of the pathogen - microbes, viruses, bacteria, fungi, etc.): also the presence of foci of chronic infection (chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, kidney pathology), surgery on the pelvic organs, etc.).
- Non -infectious (stagnant)(decrease in immunity, hypothermia, decrease in physical activity, sedentary sedentary lifestyle, long -term sexual abstinence and, conversely, excessive sexual activity, alcohol abuse, etc.).
Thus, it emphasizes that the isolated hit of the pathogen into the tissue of the organ is not always and may not necessarily be the cause of the development of the disease.The most frequently determined pathogen is E. coli (86 %), then - Klebsielly, Proteus, Enterococci, Pseudomonas stick.With regard to streptococci, staphylococci, chlamydia, mycoplasm, ureaplasm of the opinion of researchers about their significance in the development of the disease differ.It is extremely rare for the causes of prostatitis that specific pathogens become (pale treponema, a wand of Koch, etc.).
Classification
For the alleged reason, inflammation of prostatitis is divided into:
- Acute bacterial - pathogenic microflora causes serious damage to prostate tissues with a pronounced inflammatory reaction.Most often it develops with infection with gonococcus and other pathogens.
- Chronic bacterial-the association of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic bacteria causes sluggish inflammation, the activity of which remains for more than 2 months.As a rule, the pathogens are streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli, Klebsiella, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, chlamydia, herpesvirus, and yeast -like fungus of candidate.
- Chronic abacterial - in the presence of an inflammatory process in the prostate, it is not possible to detect a causal microflora.A similar form of the disease develops when urine is cast into the ducts of the prostate gland, stagnation of venous blood in the pelvis, a violation of its emptying (rare or too frequent ejaculation).In the latter case, the disease is called stagnant prostatitis.
Symptoms of prostatitis and the first signs
In a man, the first signs of prostatitis are very diverse and include a complex of violations in the seed:
- involuntary urination;
- the appearance of discomfort and pain during urination;
- frequent urination;
- soreness with prolonged sitting in the perineum;
- decrease in potency;
- urination problems, violation of erection and sexual desire, infertility;
- difficulties in urination, sensation of obstacles during urination;
- weak stream during urination;
- The sensation is incompletely emptying the bladder after urination;
- the impossibility of an erection or a decrease in the duration of an erection;
- decrease in libido;
- In some cases, male infertility is the main symptom of prostatitis.
Symptoms of acute prostatitis
There are three stages of acute prostatitis, which are characterized by the presence of a certain clinical picture and morphological changes:
- Acute catarrhal prostatitis.Patients complain of rapid, often painful urination, pain in the sacrum and perineum.
- Acute follicular prostatitis.The pain becomes more intense, sometimes radiate to the anus, intensify during defecation.Urination is difficult, urine flows with a thin stream.In some cases, urine delay is noted.Subfebrilite or moderate hyperthermia.
- Acute parenchymal prostatitis.Pronounced general intoxication, hyperthermia up to 38-40 ° C, chills.Dizuric disorders, often an acute delay in urination.Sharp, pulsating pains in the perineum.Difficulty to defecate.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis
In rare cases, chronic prostatitis becomes the outcome of an acute process, however, as a rule, chronic prostatitis with erased symptoms develops primaryly.The temperature occasionally rises to subfebrile values.A patient with chronic prostatitis notes unpleasant sensations or weak pain in the perineum, discomfort during the act of urination and defecation.The most characteristic symptom of chronic prostatitis is scarce discharge from the urethra during the act of defecation.
It should be remembered that primary chronic prostatitis develops over a significant period of time.He is preceded by prostatosis (stagnation of blood in the capillaries), gradually turning into abacterial prostatitis (the initial stage of inflammation).
Chronic prostatitis is often a complication of a chronic inflammatory process caused by the causative agent of a specific infection (chlamydia, trichomonas, ureaplasma, gonococcus).Symptoms of a specific inflammatory process in many cases mask manifestations of chronic prostatitis.It is possible a slight increase in pain during urination, weak pain in the perineum, scarce discharge from the urethra during defecation.A slight change in the clinical picture and the attachment of chronic prostatitis often go unnoticed by the patient.
Chronic prostatitis can be manifested by a burning sensation in the urethra and perineum, dysuria, sexual disorders, increased general fatigue.The consequence of potency violations (or fear of these violations) often becomes mental depression, anxiety and irritability.The clinical picture of chronic prostatitis does not always include everything, without exception, the listed groups of symptoms, differs in different patients and changes over time.
There are three main syndrome characteristic of chronic prostatitis:
- Dysurian syndrome (urination disorder).
As a result of inflammation in chronic prostatitis, the volume of the prostate squeezing the ureter increases.The lumen of the ureter decreases.A patient with prostatitis has frequent urge to urinate, a sense of incomplete emptying of the bladder.As a rule, dysuric phenomena are expressed in the early stages of chronic prostatitis.Then, compensatory hypertrophy of the muscle layer of the bladder and ureters develops.The symptoms of dysuria during this period are weakening, and then again increased during decompensation of adaptive mechanisms.
- Pain syndrome in chronic prostatitis.
There are no pain receptors in the prostate fabric.The cause of pain in chronic prostatitis becomes almost inevitable, due to the abundant innervation of the pelvic organs, involvement in the inflammatory process of the nervous paths.
Patients with chronic prostatitis complain of pain of various intensity - from weak, aching to intense, violating sleep.There is a change in the nature of pain (enhancement or weakening) with ejaculation, excessive sexual activity or sexual abstinence.Pains radiate to a scrotum, sacrum, crotch, sometimes into the lumbar region.It should be borne in mind that the lower back pain occurs not only with prostatitis.The cause of pain in this area may be osteochondrosis and a number of other diseases.
- Sexual disorders in chronic prostatitis.
In the initial stages of chronic prostatitis, dispositions can develop, which manifested differently in different patients.Patients may complain of frequent night erections, erased orgasm or deterioration of an erection.Accelerated ejaculation is associated with a decrease in the threshold level of excitement of the organ center.Pain for ejaculation can cause a patient to refuse prostatitis from sexual activity.In the future, sexual disorders become more pronounced.At the advanced stage of chronic prostatitis, impotence develops.
The degree of sexual disorder in chronic prostatitis is determined by many factors, including the sexual constitution and the psychological mood of the patient.Violations of potency and dysuria can be caused by both changes in the prostate gland and the suggestibility of the patient, who, when he is detected by chronic prostatitis, expects the inevitable development of sexual disorders and urination disorders.Especially often psychogenic display and dysuria develops in suggestible, alarming patients.
Impotence, and sometimes the very threat of possible sexual disorders, is difficult to transfer to patients with prostatitis.Often there is a change in character, irritability, grumbling, excessive concern with their own health and even “departure into the disease”.
Complications
As complications of both acute and chronic prostatitis, a number of serious diseases and conditions occur.So, in a man who was ill with prostatitis, the number of male sex hormones may significantly decrease, which causes a decrease in sexual desire.As a result, a person has constant problems with an erection.In addition, difficulties with potency in a man suffering from prostatitis can arise as a result of a number of psychological problems.
Another serious complication of chronic prostatitis is infertility, which is observed in approximately 40% of patients suffering from a chronic form of the disease.
Sometimes, the formation of stones and cysts of prostate is noted as complications of prostatitis.An even more formidable complication is prostate sclerosis: a state where the iron decreases and ceases to fully function.In this case, the patient is doomed to constant pain, urination problems, sexual disorders.
The prostate adenoma, which is benign education, also often develops precisely as a result of prostatitis.With adenoma, surgical intervention is inevitable.
The most formidable complication of prostatitis in men is prostate cancer, which is fraught with the most serious consequences.
All these complications, as well as directly by chronic prostatitis, significantly worsen the life of a man.That is why timely competent treatment of prostatitis is extremely necessary.
Photo
Diagnostics
Thanks to active agitation and ubiquitous advertising today, even schoolchildren know not only about symptoms, but also how to treat a prostate.However, the absence of any signs prevents not only to choose the right drugs, but also to make a diagnosis in time.The best way to prevent inflammation is to visit the clinic more often.Therefore, as often the diagnosis of prostatitis is carried out during a preventive examination by a urologist.
If there are complaints, an experienced doctor can already suspect the inflammation of the prostate and prescribe the appropriate tests, among which they often carry out:
- finger rectal examination;
- Analysis of secretion and seed fluid;
- ultrasound examination of the prostate;
- urine and blood analysis;
- Taking a smear from the urethra.
How to treat prostatitis?
Prostatitis in men is treated depending on the form of the disease.
Acute inflammation is an indication for the hospitalization of the patient in the urological hospital, with chronic patients undergo the course of therapy at home.If the cause of the disease was a sexually transmitted infection, both partners should take antibiotics.
Treatment of acute prostatitis
During acute inflammation, a man shows peace, complete abstinence from sex and an easily digestible diet.You should refuse alcohol, smoking, spicy spicy dishes, preservatives, fatty foods.
Medicines used for treatment in a hospital:
- AntibioticsCephalosporinal series - destructively affect most known pathogenic bacteria.The first 5 days they are administered intravenously, from the 5th to the 10th day of treatment intramuscularly;
- Antiprotozoal and antibacterial agents- accumulate in the prostate, are active in relation to the most frequent pathogens of the disease;
- Anti -inflammatory drugs(NSAID) - normalize body temperature, eliminate soreness, stop the inflammatory process.They are prescribed in the form of tablets, rectal candles, intramuscular injections (paracetamol, nimesil);
- Disinoxical solutions- accelerate the excretion of microbial toxins from the body, improve blood microcirculation in the prostate gland.Intravenous-drill are introduced;
- Blocks α1 adrenergic receptors- relax smooth muscle fibers of the prostate gland, due to which the outflow of urine restores.It is taken inside in the form of tablets.
This is how the basic treatment regimen looks, which the doctor supplements, if necessary, other medicines for prostatitis.It is important to completely undergo a course of therapy in order to minimize the risk of chronic process.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
Therapy of chronic prostatitis directly depends on what stage the disease is located.If the disease exacerbates, then treatment is similar to treatment with acute bacterial prostatitis.
When the disease is in the remission stage, the man will experience the following symptoms:
- Minor painful sensations that occur rarely, but regularly;
- A feeling of severity in the area of the prostate, the lumbosacral zone, in the genital area;
- In some cases, dysuric disorders are joined: increased urge to urination, pain during emptying of the bladder, etc.;
- Perhaps a deterioration in psycho -emotional well -being, depressive moods against the background of which sexual failures happen.
There are a number of contradictions in the issue of chronic inflammation therapy.Scientists have not yet come to a consensus regarding whether antibiotics should be prescribed, or this is not necessary.Those experts who insist on taking antibacterial drugs believe that the bacterial flora in a secret taken for analysis could simply not get.
Another, and most of the scientists indicate that the antibiotic must be taken only if the bacterial flora has been isolated.Abacterial prostatitis with the lack of symptoms is not treated with antibacterial agents.
They offer the following patient tactics:
- Course Reception of NSAIDs.
- The appointment of funds aimed at normalizing the outflow of lymph and to improve blood microcirculation in the organ.
- Reception of immunomodulator drugs.
- To eliminate the problems with the erection, the use of antidepressants and sedatives is shown.
- To strengthen the pelvic muscles, regular physical activity helps normalize blood circulation.It is best if it is a specially compiled complex of physiotherapy exercises.Physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect-rectal electrophoresis, transrectal microwave hyperthermia, UHF, magnetic laser therapy, etc. These procedures help get rid of pelvic pain syndrome.
Starting the treatment of chronic prostatitis at home, you should tune in to a long struggle, since it is not always possible to cure it in a few weeks or even months.It is recommended to combine various methods and tools for therapy, it is useful to enhance drug therapy with households.With stagnant prostatitis, regular sex is needed, interrupted sexual acts are unacceptable.
The psycho -emotional background of the patient is important: depression, depression, problems in personal life and sexual sphere are able to negate all the efforts of doctors.
Physiotherapy and prostate massage
Prostate massage.Currently, it is one of the main techniques in the treatment of prostatitis.Many experts believe that treatment of prostatitis without this procedure is impossible at all.However, there are no reliable clinical data about how effective the massage is not.Many patients note a significant improvement in their own state according to many criteria after a massage course.Therefore, let's consider the methodology of this procedure and the mechanism of its therapeutic effect.
To carry out the procedure, the patient occupies a knee-elbow pose.Thanks to this position, the muscles of the pelvis are relaxed as much as possible.The doctor puts on rubber gloves, the index finger of the gloves is lubricated with a special gel -shaped lubricant.The index finger is neatly inserted into the anus of the anus.Next, you should feel the front wall of the rectum.Having groped for the prostate, the urologist produces strokeing pressing.
Thanks to pressure on the prostate gland, mechanical squeezing of the gland secret in the urethra occurs.On the urethra, an outflow of the latter occurs.It is recommended every time after prostate massage to conduct a microscopic analysis of the prostate secret to assess the dynamics of the process.
However, the allocation of the secret of the prostate is not the only positive effect in massage.Also, circulatory is activated in the prostate gland, which leads to an improvement in infection resistance and accelerating the restoration of damaged tissues.
Microwave microwave therapy.The local exposure to high -high frequency electric waves leads to an increase in temperature in the warmed area.With an increase in the local temperature to a level of 39-40 degrees, blood flow expansion, blood flow, attracting immune cells to the focus and their activation to combat infection.Also, an increase in temperature leads to a decrease in spasm of smooth muscles, which leads to better drainage of the prostate secret and a decrease in pain.
Diet
Diet for prostatitis in men is based on the principles of healthy diet and limiting harmful foods.The diet is selected taking into account the severity of the manifestation of the disease and the characteristics of the body.All products that cause allergies or exacerbation of symptoms fall under the ban.
Basic principles of diet:
- adding garlic and onions to dishes, mustard;
- compilation of the menu, taking into account the phase of exacerbation;
- rejection of any type of alcohol and smoking;
- exclusion from the diet of spices, preservatives, semi -finished products, sharp and salty dishes;
- regular meals, preferably at the same time;
- complement the diet with physical exercises and walking;
- rejection of fat and smoked dishes;
- consumption of vegetable salads, herbs;
- minimal heat treatment of fruits and vegetables;
- restriction of salt and sweets;
- Constant maintenance of a diet and rejection of harmful products.
Useful food:
- a variety of soups (rich broths are undesirable);
- cereals (oatmeal, millet, buckwheat, and others), pasta, spaghetti;
- Fat vegetables (olive oil is highly recommended);
- fresh herbs, fruits and vegetables (melons and watermelons, zucchini and pumpkin, parsley and salad, peas green and cauliflower, cucumbers and tomatoes, beets, potatoes and carrots);
- products of the sour -milk group (bifido, yogurt, ayran, cottage cheese, fermented, kefir, sour cream);
- low -fat meat and ocean fish;
- Gray bread;
- dried fruits;
- honey.
One of the very important substances in the prevention of prostatitis is zinc, so you often need to consume healthy seafood, pumpkin seeds that have a lot of zinc, white poultry, walnuts and beef.
How to prevent the development of prostatitis at any age?
- The use of barrier methods of contraception (condom), especially when it comes to anal sex;
- Timely treatment of STIs;
- Regular sex life, bringing relationships to full ejaculation;
- The prevention of crotch injuries, when classes, traumatic sports should be used by all possible methods of protection;
- Compliance with personal hygiene;
- Ensuring sufficient physical activity.
Despite the fact that today prostatitis is not associated with the risk of developing adenoma or prostate cancer, the disease brings a lot of suffering to its owner.A man exhausted by chronic pain, feeling his sexual weakness, tired of prolonged treatment, changes noticeably externally and experienced doctors define such patients at first glance.To avoid such a fate, you should be careful about your health, carefully protected with every new partner and treat sexually transmitted diseases in time.
Prostatitis is not completely treated in all cases, but an experienced urologist is able to significantly improve the patient's condition and the quality of his life.